BUSY? ON THE ROAD? PREFER LISTENING TO READING? TUNE INTO THE PODCAST EDITION! Public broadcasters …
Busy? On the road? Prefer listening to reading? Tune into the podcast edition!
Twitter is an increasingly important platform for traditional media outlets to broadcast content through. The pervasiveness of the internet in people’s lives means that journalists are forced to use the platform if they want to connect with an audience. In the days of print media, a single broadcast gave no opportunity for discourse or communication between publisher and reader, with Twitter, users have the power to interact with global leaders (Carmody, 2019).

Image By Soryn via Adobe Stock.
News reports and current affairs report in real-time on Twitter, yet the propensity for the platform to spread ‘fake news’ and misinformation (Langin, 2019) remains a headache for Twitter management and legislators to resolve.
As I am an aspiring journalist, I find the absence of editorial oversight on Twitter to be a concern. Twitter uses an algorithm; my research suggests there is an apparent lack of academic research to grasp the long-term implications of millions of users accessing and publishing data that has been ranked by artificial intelligence (AI). The lack of regulatory framework over Twitter means that it is self-censoring, according to CEO Jack Dorsey the company is behind on how it is to apply effective use of AI to fight abuse on the platform (Roettgers, 2019).
This blog entry investigates the key concepts surrounding the influence of Twitter on modern journalism.
How has Twitter had an impact on modern journalism?
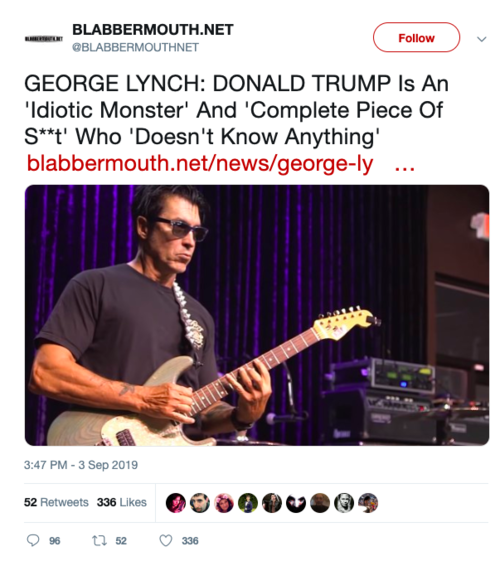
The tweet pictured drew a considerable response. It is a clickbait-style tweet using content taken from an interview I conducted with guitarist George Lynch.
Twitter has been a phenomenon in post-modern Technoculture, which references how technology appears in literature since the industrial revolution. Canadian philosopher Marshall McLuhan posits that a medium itself shapes and controls “the scale and form of human association and action” (Understanding Media: The Extensions of Man, 1.) and likens the light globe to a medium without any content as it enabled people to gather at night and exchange ideas. In this way, Twitter is a medium that offers the most significant opportunity to share information quickly, to anyone, anywhere.
A lack of accountability in e-communications has led to accusations that Twitter is dehumanising (Gourguechon, 2019). In the lead up to the 2020 elections in the United States, Twitter will feature in the spread of misinformation (“Get ready for more humanlike bots, better deep-fake videos and wall-to-wall disinformation in 2020 race”, 2019) It has become disarmingly tricky to determine which news sources to trust on Twitter as it has been at the frontline in the shift away from traditional media sources.
I have used Twitter extensively for over three (3) years. As a broadcaster for 4ZZZ and as a podcast host, third-party websites have taken content from my interviews and broadcast them over twitter in a manner designed to attract as much attention as possible (ala ‘clickbait’).
Twitter has become driving in force in initiating social movements and agitating for change in society. The adaptation of #BlackLivesMatter by users to highlight the perception of the perversion of justice toward minority communities was made more potent by the adaptation of the hashtag (#). Twitter acted as the central plank in raising awareness of episodes (Cohen, 2019) a role that would traditionally have been filled by news media. Without editorial oversight from a trusted masthead, Twitter users focused on the most inflammatory aspect of an incident and used that to spread misinformation (Clifton, 2019). Twitter is an example of technological determinism, a term which American sociologist Thorstein Veblen coined (“Technological Determinism”, 2019) to try and comprehend the degree in which technology influences human thought.
This is a video of the story of how #BlackLivesMatter forced America to confront racism once more using the power of social media, from the activists who helped create it. Featuring DeRay Mckesson, Opal Tometi and Kwame Rose.
Twitter is an example of technological determinism, a term which American sociologist Thorstein Veblen coined (“Technological Determinism”, 2019) to try and comprehend the degree in which technology influences human thought.
Is Twitter more powerful than news media outlets?
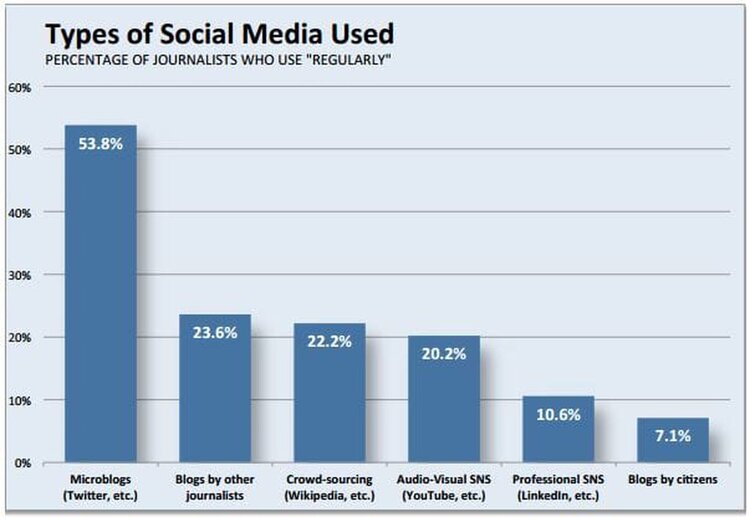
Image by University of Indiana School of Journalism via The Washington Post (2014)
The influence of Twitter has overtaken the power of traditional media on markets (Milas, Panagiotidis & Dergiades, 2019). As an agent of change, Twitter is a disruptive innovation which has shifted the method in which users obtain news they would traditionally have sourced through news media. As far back as 2012, Over 50% of people have learned about breaking news via social media rather than official news sources, and ‘fake news’ is reported to be 70% more likely to be shared by users (Lohr, 2019). Before Twitter, journalists communicated in a one- dimensional manner. Twitter’s introduction of the @ symbol allowed users to identify each other, readers responded to journalists and dialogue was possible. When Everett Rogers proposed his Diffusion of innovations theory in 1962, Twitter was 44-years away from its launch. Twitter added five million daily users in Q3 FY19 to bring its total users to 139 million (Kastrenakes, 2019) and continues to maintain users and grow its subscriber base. Twitter’s growth supports Rogers theory of the four main elements that influence the spread of a new idea or concept: the innovation itself, communication channels, time, and a social system.
The 2016 Presidential election campaign in the United States changed the perception in the manner in which successful campaign messages broadcast. Campaign messages sent over twitter resonate with voters the same as traditional media sources such as the NY Times or Washington Post. That Donald Trump found significant favour with voters, could have been through his prolific use of Twitter.
How has twitter disrupted modern journalism?

Image by Twitter via Twitter brand resources.
The convergence of print News media onto the internet, then through social media platforms such as Twitter has given the unprecedented public access to information and has been likened to a global ‘town square’ (Leetaru, 2019). The key benefit to Twitter is that information can broadcast in real-time; there is no need to produce a news bulletin with a headline. Traditional media outlets have been sourcing copy from Twitter, and it is considered an ‘elite channel’ compared to Facebook. The potential is there for Twitter to offer unprecedented reach for news media outlets; however, the public knows very little about the algorithms used by Twitter to promote and de-platform conversations, and according to (Darcy, 2019), Twitter’s algorithm amplifies extreme political rhetoric. Twitter’s global head of content Kay Madati does not see the conflict between his company and traditional media sources, claiming that Twitter provides an opportunity for companies to make content that reaches more people. However, traditional media must compete with the rise of user-created content.
As a journalist, I believe the blurred line between reporting and advocacy is a concern. The challenge as I see it is to continue to strike a balance and not veer into partisanship as Fox/ Sky News and CNN have done. However, the drive into partisan politics by the networks has given them a rating spike, bringing advertisers and sponsorship funds. Alarmingly, Pew research (Wojcik & Hughes, 2019) found that the most prolific Twitter users in the United States generate 80% of all tweets, and they are more likely to engage in politics.
The internet and world wide web offer access to any market in the world for vendors; defined as Digital capitalism, it has disrupted ‘bricks and mortar’ service industries and driven the change from print media to e-media. This shift has made a profound impact on news sources; many print media companies have either closed shop or amalgamated. Twitter offers news at no subscription cost to the user, further lancing the paid print model, and presenting many challenges for mastheads as they negotiate paid subscription models. In industrialised Western economies, the economic framework of trade is called Advanced capitalism, given capitalism’s pervasive influence over society. Entrepreneurs and commercially savvy businesses leverage the power of the internet to reframe market needs by shifting solutions from products to services, highlighting the importance of knowledge and intellectual property (IP) over fixed assets and intelligence (the shift from operational expenditure to capital expenditure). This scenario gives the ‘Knowledge worker’ distinct advantage in markets driven by information technology (Ware & Degoey, 2019)
Does Twitter enable the knowledge economy?
An economy where knowledge is the greatest asset presents tremendous opportunities for a journalist. Tweets with video content attract ten-fold the attention of other content, and with 93% of these videos viewed on mobile devices (Cooper, 2019) the appetite for journalists to curate meaningful content has never been higher, and this is something that I have incorporated into my journalism strategy.

Image by By HANK GREBE via Adobe Stock.
From FY15, onward Twitter has given journalists a potential audience of over 300 million users (“Twitter: number of active users 2010-2019 | Statista”, 2019). If traditional news media mastheads embrace Twitter, it can act as a vital pillar in an organisation’s news strategy. However, the ongoing challenge is twofold; Gaining the intelligence sufficient to justify significant investment in advertising on Twitter is difficult due to the platform’s opaque algorithm. Secondly, the volume of users with the propensity for broadcasting information that isn’t fact-checked means that credible news sources are potentially competing for readership with fake news.
In my view, until the United States Congress issues practical regulatory framework, which Twitter is bound to follow under governance; Twitter will continue to be both a source of concern and an opportunity for journalists to maintain the news media tradition.
If you enjoyed reading this post, you can drop me a line and says hello on Twitter.
REFERENCES
Carmody, B. (2019). ABC comedy to interrogate outrage culture, identity politics. Retrieved 1 October 2019, from https://www.brisbanetimes.com.au/culture/tv-and-radio/new-abc-comedy-to-interrogate-outrage-culture-and-identity-politics-20190926-p52v4d.html
Clifton, D. (2019). Russian trolls stoked anger over Black Lives Matter more than was previously known. Retrieved 9 October 2019, from https://www.motherjones.com/politics/2018/01/russian-trolls-hyped-anger-over-black-lives-matter-more-than-previously-known/
Cohen, D. (2019). The #BlackLivesMatter Hashtag Has Been Used on Twitter Almost 30 Million Times. Retrieved 9 October 2019, from https://www.adweek.com/digital/the-blacklivesmatter-hashtag-has-been-used-on-twitter-almost-30-million-times/
Darcy, O. (2019). How Twitter’s algorithm is amplifying extreme political rhetoric. Retrieved 9 October 2019, from https://edition.cnn.com/2019/03/22/tech/twitter-algorithm-political-rhetoric/index.html
Get ready for more humanlike bots, better deep-fake videos and wall-to-wall disinformation in 2020 race. (2019). Retrieved 9 October 2019, from https://www.baltimoresun.com/opinion/columnists/zurawik/bs-ed-zontv-media-disinformation-20190905-q7jmn5ai2vhq3iiyxyrzowokky-story.html
Gourguechon, P. (2019). As Trolls Trash Twitter CEO @Jack, Social Science Explains Why People Are So Mean Online. Retrieved 9 October 2019, from https://www.forbes.com/sites/prudygourguechon/2018/09/17/twitter-jack-dorsey-why-are-people-so-mean-on-social-media/#567e7540747a
Kastrenakes, J. (2019). Twitter’s growth looks way better now that it’s hiding monthly usage numbers. Retrieved 9 October 2019, from https://www.theverge.com/2019/7/26/8929933/twitter-q2-2019-earnings
Langin, K. (2019). Fake news spreads faster than true news on Twitter—thanks to people, not bots. Retrieved 8 October 2019, from https://www.sciencemag.org/news/2018/03/fake-news-spreads-faster-true-news-twitter-thanks-people-not-bots
Leetaru, K. (2019). Mapping Where Twitter Reaches—and Where It Doesn’t. Retrieved 9 October 2019, from https://www.theatlantic.com/international/archive/2015/08/twitter-global-social-media/402415/
Lohr, S. (2019). It’s True: False News Spreads Faster and Wider. And Humans Are to Blame. Retrieved 9 October 2019, from https://www.nytimes.com/2018/03/08/technology/twitter-fake-news-research.html
McLuhan, M. (1964). Understanding Media: The Extensions of Man, 1.
Roettgers, J. (2019). Twitter CEO Jack Dorsey Says Company Is Behind on Using AI to Fight Abuse. Retrieved 8 October 2019, from https://variety.com/2018/digital/news/twitter-ceo-jack-dorsey-says-company-is-behind-on-using-ai-to-fight-abuse-1202980959/
Technological Determinism. (2019). Retrieved 9 October 2019, from https://www.communicationtheory.org/technological-determinism/
Twitter: number of active users 2010-2019 | Statista. (2019). Retrieved 9 October 2019, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/282087/number-of-monthly-active-twitter-users/
Ware, J., & Degoey, P. (2019). Knowledge Work and Information Technology. Retrieved 9 October 2019, from http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.25.3110&rep=rep1&type=pdf